(Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, Wix)
Achieving accurate conversion tracking has become increasingly challenging due to browser privacy updates, ad blockers, and limitations of client-side tracking. Server-side Google Tag Manager combined with Stape Store provides a reliable framework to recover lost conversions, improve attribution accuracy, and ensure consistent data delivery across marketing and analytics platforms.
In this guide, we focus specifically on Shopify to explain the complete implementation in detail. However, the same underlying methodology—using server-side tracking, persistent identifier storage, and webhook-based fallback logic—can be applied to other platforms such as WooCommerce, Magento, and Wix, SquareSpace with minimal adaptation.
The concepts covered here are platform-agnostic. Once you understand the Shopify implementation, extending the setup to other eCommerce systems becomes largely a matter of adjusting event sources and webhook payloads rather than rethinking the tracking architecture.
Why Shopify Tracking Still Loses Data
Even with Shopify’s Web Pixel API, some conversions fail to reach analytics or ad platforms. Common causes include:
- Browser privacy features blocking identifiers or cookies
- Ad blockers preventing client-side tags from firing
- Network issues or page unloads during checkout
- Device or browser-specific execution failures
The Core Idea: Server Side tracking with webhook and Stape store
The strategy is straightforward:
- Track purchases normally via the browser and server-side GTM.
- Persist key identifiers and cookies in a server-side storage layer.
- Use Stape Shopify webhooks as a guaranteed fallback for every completed order.
- Check whether a purchase was already tracked.
- Only send server-side conversions when the browser-based event fails.
This ensures every valid order is reported exactly once—no gaps, no duplicates.
Step 1: Implement a Complete Web and Server-Side Tracking Foundation
Start by establishing a solid tracking foundation using both web-based Google Tag Manager and server-side GTM. All core Shopify eCommerce events should be implemented and validated across the funnel to ensure consistent data flow from product interaction through purchase completion.
At a minimum, this includes tracking the following events:
- view_item – triggered when a user views a product detail page
- add_to_cart – fired when a product is added to the cart
- view_cart – captures cart page views and updates
- begin_checkout – triggered when the checkout process starts
- purchase – recorded at order completion
Each of these events should be forwarded from the web container to the server-side GTM container, where they are processed and sent to analytics and advertising platforms. Server-side processing ensures greater resilience against ad blockers, browser privacy restrictions, and client-side execution failures.
Before proceeding to advanced logic or fallback mechanisms, confirm that all events are firing correctly, carrying the required parameters (product data, value, currency, and identifiers), and are being received by the server container. A fully functional baseline setup is critical for achieving reliable and scalable Shopify tracking
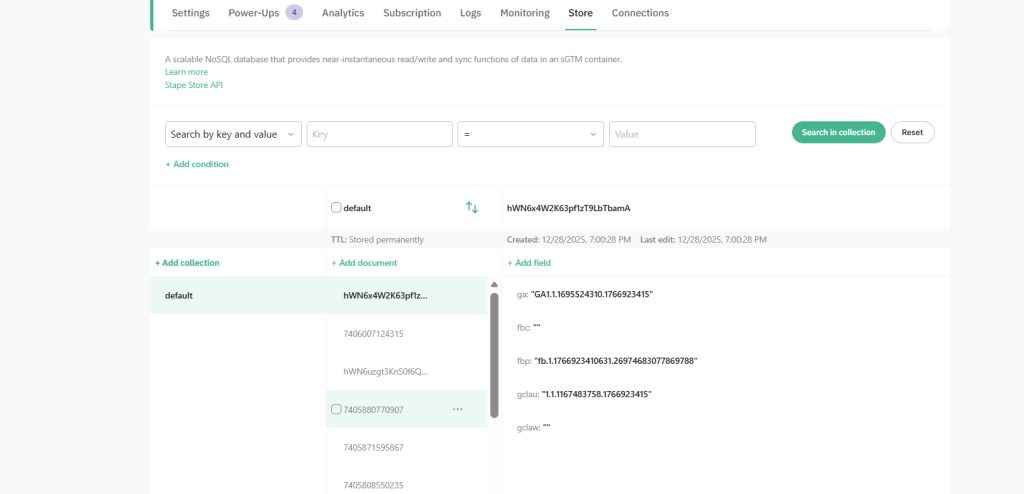
Step 2: Store Critical Cookies Server-Side Stape Store
To enable accurate fallback reporting, you must persist marketing identifiers—such as Meta fbclid, gclid —on the Stape Store.
This is typically done at the begin_checkout or add_to_cart stage, when a stable checkout or cart identifier becomes available. These identifiers act as stitching keys, allowing you to later associate webhook-based orders with the correct user and session data.
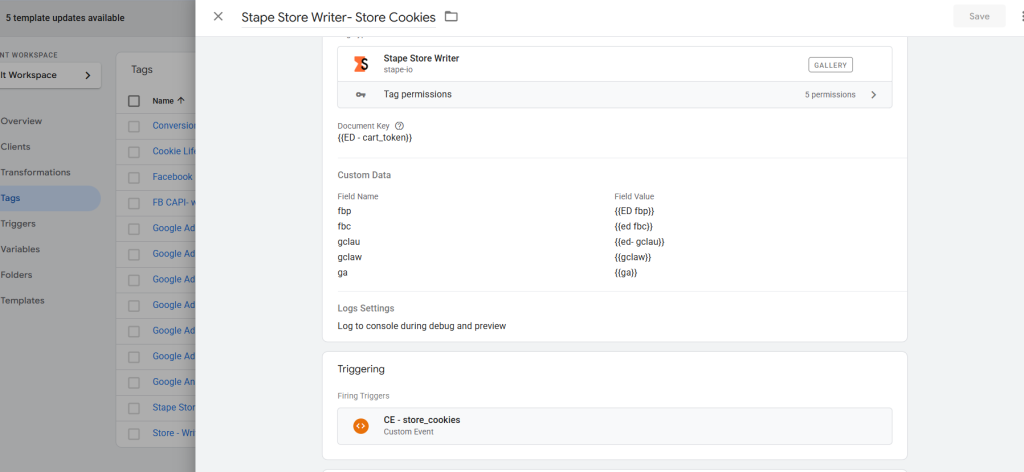
Cookies are sent from the Shopify web pixel to the server container and stored securely. If consent management is in place, consent status should be stored alongside these identifiers to ensure compliance.
Step 3: Log Successfully Tracked Purchases on Stape Store
Every purchase that is successfully reported through the browser should be recorded server-side using the transaction ID as a unique key.
This creates a reference ledger of already-processed orders. Later, when a webhook arrives, the system can determine whether the purchase has already been tracked and avoid duplicate reporting.
Step 4: Configure Shopify Order Webhooks on Stape App
Shopify Stape webhooks provide a reliable, backend-generated signal for every completed order. These can be configured in Stape App.
To ensure correct sequencing, it is recommended to delay at least 1 min for webhook processing slightly so browser-based events have time to reach the server first.
Step 5: Validate and Recover Missing Conversions
When an order webhook is received:
- Check whether the transaction ID already exists in Stape Store via Stape lookup Variable template
- If it exists, the conversion has already been tracked—no action needed.
- If it does not exist, process the webhook as a fallback conversion.
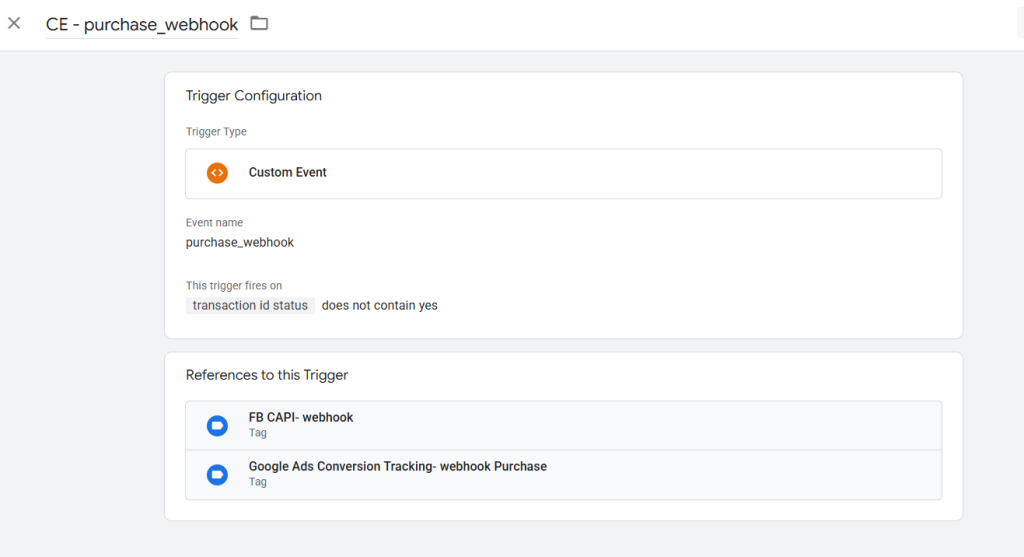
At this stage, previously stored cookies( fbclid,gclid,ga) are retrieved via the Stape lookup table and injected into server-side conversion tags (such as Meta CAPI or Google Ads) via transformation feature on server side GTM . This preserves attribution quality and allows platforms to correctly associate the purchase with prior ad interactions.
Extending the Model to Other Platforms
Once this architecture is in place, it can be extended to additional platforms such as:
- Google Ads (including offline conversions or adjustments)
- GA4
- TikTok
- Snapchat
- Other CAPI-based systems
The principle remains the same: store identifiers early, validate transactions, and only recover conversions when needed.
Final Thoughts
This server-verified tracking approach closes the gaps left by client-side limitations and ensures Shopify merchants capture the full value of their marketing data. By combining web events, server-side storage, and webhook validation, you can dramatically improve conversion accuracy, attribution reliability, and campaign performance.
