Dynamic remarketing enables advertisers to deliver highly personalized ads by automatically tailoring creative based on a user’s previous interactions with a website. Instead of showing generic ads, dynamic remarketing allows you to display the exact products or services a user viewed, added to cart, or purchased—significantly improving relevance and conversion rates.
This article explains how dynamic remarketing works, how to set it up using the Google tag, and how to correctly implement events and parameters for accurate tracking and ad personalization.
What Is Dynamic Remarketing?
Dynamic remarketing uses data collected from your website to automatically generate ads that reflect a user’s prior behavior. For example:
- A retail visitor sees ads featuring products they viewed.
- A travel shopper sees ads for routes they searched.
- A user who abandoned a cart sees reminders with the exact items left behind.
To achieve this, Google Ads relies on:
- The Google tag installed on your website.
- Event-based tracking that captures user actions.
- A business data feed or Google Merchant Center feed that contains product or service details.
Before You Begin
To enable dynamic remarketing, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Google tag is installed across all relevant pages of your website.
- Event tracking is implemented to capture meaningful user interactions.
- A feed is configured (e.g., Merchant Center or business data feed) with attributes such as product ID, price, image, and landing page URL.
- Feed attributes match event parameters exactly to allow Google Ads to retrieve the correct items.
Without proper alignment between your site data and your feed, dynamic ads cannot render correctly.
How to Set Up Dynamic Remarketing
Dynamic remarketing works by sending event data from your website to Google Ads whenever users take specific actions. These events help Google assign users to automatically generated audience segments (formerly known as remarketing lists).
Step 1: Implement the Google Tag
The Google tag collects interaction data and sends it to Google Ads. This tag must fire on every page where user activity should be tracked.
Step 2: Track Dynamic Remarketing Events
Dynamic remarketing events represent meaningful user actions, such as viewing a product or completing a purchase. Each event includes:
- An event name (what action occurred).
- A set of event parameters (details about the product or service).
Anatomy of a Dynamic Remarketing Event
A dynamic remarketing event consists of two core components:
1. Event Name
The event name identifies the type of interaction. Google recommends using standardized event names so users can be automatically added to the correct “your data” segments.
Required event for dynamic remarketing:
| view_search_results | This event measures when a user visits a search results page. |
| view_item_list | This event measures when a user visits a category page. |
| view_item | This event measures when a user visits a product page. |
| add_to_cart | This event measures when a user adds an item to the shopping cart. |
| purchase | This event measures purchases. |
2. Event Parameters
Event parameters provide context about the interaction. At a minimum, every dynamic remarketing event must include an items array containing one or more item objects.
Each item object typically includes:
- A primary identifier (such as id, origin, or destination)
- The google_business_vertical parameter
- Optional value-related fields, such as price or total transaction value
Example: Tracking Product Views in Retail
Below is an example of tracking a user who viewed two products on an eCommerce site:
<script>
gtag(‘event’, ‘view_item’, {
‘value’: 998.55,
‘items’: [
{
‘id’: 1234,
‘google_business_vertical’: ‘retail’
},
{
‘id’: 45678,
‘google_business_vertical’: ‘retail’
}
]
});
</script>
In this example:
- The event name is view_item.
- The items array contains two product IDs.
- The value parameter represents the total value of the viewed products.
view_item event
add_to_cart event:
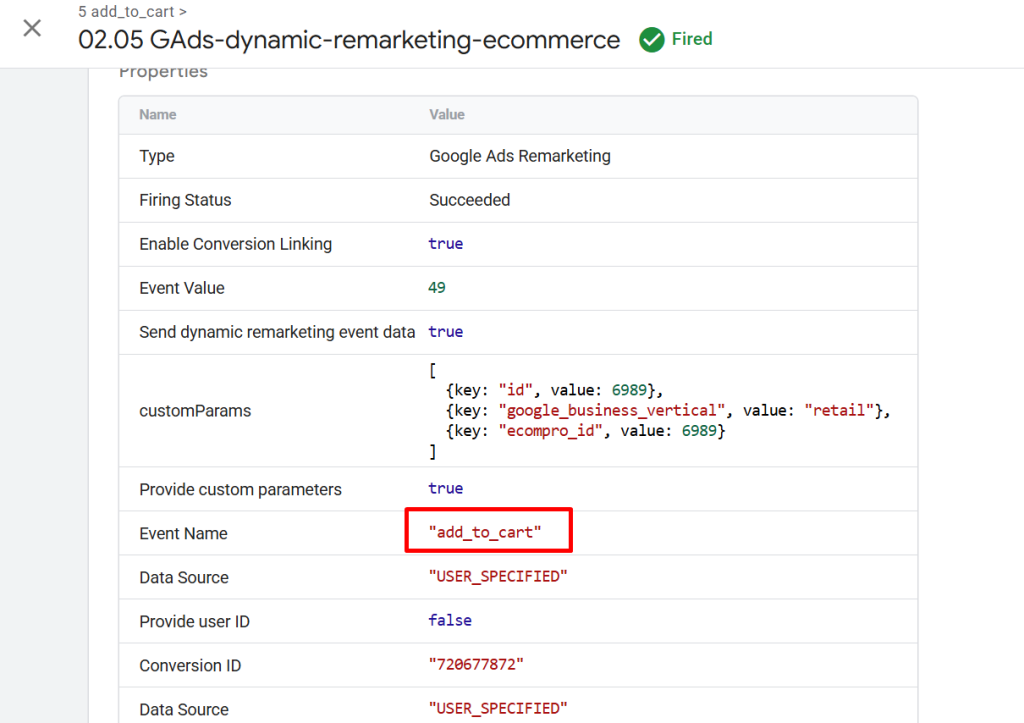
Feed Matching and Business Verticals
Google Ads uses item parameters to generate feed keys, which are then matched against your business data feed or Merchant Center feed. For this to work:
- Event parameter values must exactly match feed attribute values.
- The correct google_business_vertical must be specified (e.g., retail, flights, hotels).
Example: Dynamic Remarketing for Travel (Flights)
For travel advertisers, feed keys are often constructed using multiple parameters, such as origin and destination.
<script>
gtag(‘event’, ‘purchase’, {
‘value’: 639.74,
‘items’: [{
‘origin’: ‘LHR’,
‘destination’: ‘LAX’,
‘start_date’: ‘2019-04-20’,
‘end_date’: ‘2019-04-21’,
‘google_business_vertical’: ‘flights’
}]
});
</script>
In this scenario:
- Google Ads creates a feed key using origin + destination.
- The key is matched against the Flights feed.
- Ads are dynamically generated for flights from London (LHR) to Los Angeles (LAX).
Best Practices for Dynamic Remarketing Events
- Always pass at least one item object with each event.( example: id)
- For pages with many products, pass only the most relevant items to promote.
- Ensure exact consistency between feed attributes and event parameters.
- Use valid Unicode characters and avoid control or private-use characters.
- Regularly verify tag firing and parameter values using Google Tag Assistant or Google Ads diagnostics.
Common Dynamic Remarketing Setup Issues
- Mismatched IDs between the website and Google merchant feed
- Missing google_business_vertical parameter
- Incorrect or unsupported event names
- Google tag not firing on all relevant pages
- Invalid characters in parameter values
Identifying and correcting these issues early can prevent lost audience data and underperforming campaigns.
Final Thoughts
Dynamic remarketing is a powerful capability within Google Ads, but its effectiveness depends entirely on accurate tagging, consistent data, and proper feed integration. By implementing recommended events, passing correct parameters, and validating your setup, you can deliver highly relevant ads that align closely with user intent—and drive stronger results.
For ongoing optimization, regularly review audience reporting within Google Ads, monitor new terminology updates, and stay informed about evolving advertising policies and personalization guidelines.
Need help with Google Ads Dynamic Remarketing setup? Email us at support@optizent.com or fill out the contact us form.
